When The Doctor in Dr Who knows their time is up – usually because they’ve been injured so badly that they are dying – like all Time Lords, they can regenerate. They transform into a completely different body. They ends up with a new personality, new looks, a new gender, even new teeth. Could humans one day regenerate too?
Your body is constantly regenerating itself too. New cells are born to replace the ones that die. Your hair, nails and skin are always growing and renewing. Every year, you lose and regain so much that you could make a pile of dead cells that would weigh the same as your body. And yet with all this change, every morning you look in the mirror and you look and feel the same. No new personality, no new teeth. How does the human body keep such incredible control?
Here’s another puzzler. Even though our cells are always being renewed, you can’t regrow your arm if it gets cut off. We know it’s not impossible to regrow body parts: we do it for small things like cells, including whole toe nails and some animals like lizards can regrow tails. Why can we regrow some things but not others?
Creation of the shape
All of those questions are part of a field in biology called morphogenesis. The word is from Greek, and it means ‘creation of the shape’. Scientists who study morphogenesis are interested in how cells come together to create bodies. It might sound a long way from computing, but Alan Turing became interested in morphogenesis towards the end of his life. He was interested in finding out about patterns in nature – and patterns were something he knew a lot about as a mathematician. A paper he wrote in 1951 described a way that Turing thought animals could form patterns like stripes and spots on their bodies and in their fur. The mechanisms he described explain how uniform cells could end up turning into different things so not only different patttens in different places, but different body parts in different places. That work is now the foundation of a whole sub-discipline of biology.
Up for the chop
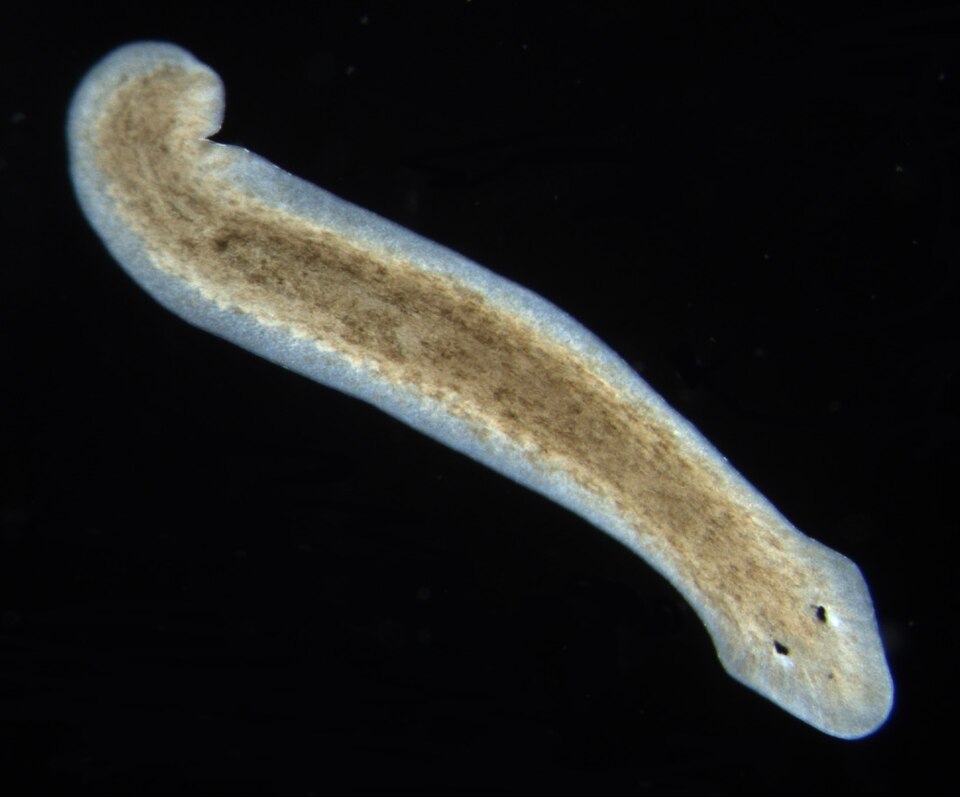
Turing died before he could do much work on morphogenesis, but lots of other scientists have taken up the mantle. One of them is Alejandro Sánchez Alvarado, who was born in Venezuela but works at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research in Kansas City, in the US. He is trying to get to the bottom of questions like how we regenerate our bodies. He thinks that some of the clues could come from working on flatworms that can regenerate almost any part of their body. A particular flatworm, called Schmidtea mediterranea, can regenerate its head and its reproductive organs. You can chop its body into almost 280 pieces and it will still regenerate.
A genetic mystery
The funny thing is, flatworms and humans aren’t as different as you might think. They have about the same number of genes as us, even though we’re so much bigger and seemingly more complicated. Even their genes and ours are mostly the same. All animals share a lot of the same, ancient genetic material. The difference seems to come from what we do with it. The good news there is that as the genes are mostly the same, if scientists can figure out how flatworm morphogenesis works, there’s a good chance that it will tell us something about humans too.
One gene does it all
Alejandro Sánchez Alvarado did one series of experiments on flatworms where he cut off their heads and watched them regenerate. He found that the process looked pretty similar to watching organs like lungs and kidneys grow in humans as well as other animals. He also found that there was a particular gene that, when knocked out, takes away the flatworm’s ability to regenerate.
What’s more, he tried again in other flatworms that can’t normally regenerate whole body parts – just cells, like us. Knocking out that gene made their organs, well, fall apart. That meant that the organs that fell apart would ordinarily have been kept together by regrowing cells, and that the same gene that allows for cell renewal in some flatworms takes care of regrowing whole bodies, Dr Who-style, in others. Phew. A lot of jobs for one gene.
Who knows, maybe Time Lords and humans share that same gene too. They’re like the lucky, regenerating flatworms and we’re the ones who are only just keeping things together. But if it’s any consolation, at least we know that our bodies are constantly working hard to keep us renewed. We still regenerate, just in a slightly less spectacular way.
– the CS4FN team (updated from the archive)
More on …
Subscribe to be notified whenever we publish a new post to the CS4FN blog.
This blog is funded by EPSRC on research agreement EP/W033615/1.


