Computing- and food-themed post on cookies and spam + a puzzle.
Welcome to Day 9 of our CS4FN Christmas Computing Advent Calendar. Every day between now and Christmas we’ll publish a post about computer science with a puzzle to print and solve. You can see all our previous posts in the list at the end.
Today’s post is inspired by the picture on the advent calendar’s door – a gingerbread man, so we have a food-themed post. Well… food-ish.
1. Cookies, but not the biscuit kind
Imagine you have a Christmas gift voucher and want to spend it in an online shop. You visit the website and see an item you’d like so you click ‘add to basket’ and then look for some other things you’d like to buy. You click on another item to find out more about it but suddenly your basket is empty! Fortunately this doesn’t usually happen thanks to cookies, which are tiny computer files that can make your website visit run smoothly.
Websites ask you if they can put these cookies on your computer. If you say ‘yes’ that lets them see that you are the same person as you add new things to your basket. It would be no use if you added your second item and the website decided that you were now a completely different person. Some cookies help the organisation know that you’re still you, even when you’re viewing lots of different pages on their website.

Other cookies mean that you don’t have to keep logging in every time you click on a new page within the website. It would be very annoying if you had to do that.
Some cookies are there to help the organisation itself. They let them see what people are clicking on when they’re on the organisation’s website, and what path they follow as they visit different pages. They can also tell what device someone is using (a phone or a computer) so they can make sure the information is set to be the right size on their screen.
If people are logged in then the website knows who they are. Because of this, organisations have to be very careful about how they use this information, to protect their visitors’ privacy. If they don’t take care then they are breaking the law and can be fined a lot of money.
Further reading
Cookies (no publication date given) – from the ICO – the Information Commissioner’s Office.
2. The recipe for spam
These days when people talk about “spam” they are talking about unwanted emails from strangers. The word spam comes from a tinned meat product which, because of a comedy sketch by Monty Python, now also means “email messages that no-one can avoid”.
by Paul Curzon, QMUL. This post was originally published on the CS4FN website.
Fighting spam

Shutting down spammers is tough for the authorities, so the internet’s arteries go on getting plugged up by spam. The best strategy against it so far seems to be filtering out junk emails from your inbox. Lots of early spam filtering relied on keeping lists of words that appear in spam and catching emails that contained them, but there were plenty of problems. For one thing, certain words that turn up in spam also appear sometimes in normal emails, so perfectly innocent messages sometimes ended up in the spam filter. What’s more, spammers have ways of eluding filters that simply check words against a list. Just me55 a-r-0-u-n-d w1th teh sp£lling.
Finally a simple but ingenious idea surfaced: instead of trying to keep a list of spammy words, why not try and teach computers to recognise spam for themselves? There’s a whole branch of maths about probability that researchers began to apply to spam, and a programmer called Paul Graham made the strategy famous in 2002 when he wrote an essay called A Plan for Spam.
Spammy maths
Paul Graham suggested that you could analyse the words you get in a sample of your email to see what the chances are that a particular word would appear in your real messages. You could do the same with a sample from your spam. Then you could look up any word in a new message and see whether it’s likely to be spam or your real email.
Of course, one word’s not enough to base your conclusion on, so Paul’s filter chose the fifteen most interesting words to look at. What that meant was that it grabbed the biggest clues to look at – words that, statistically, had the best chance of being in either spam or real mail, but not both. Then it used those clues to figure out the overall chance that an email is spam. It did this with an equation called Bayes’ theorem, which tells you how to figure out the chances of something being true given a set of facts. In this case Bayes’ theorem figures out the chances of a message being spam given the set of words in it.
What’s brilliant about the statistical approach is that not only does the computer learn as it goes on, meaning it keeps up with spammers’ tricks automatically, it can learn what words are normal for each person’s email, so scientists working on Viagra wouldn’t have to worry about all their emails going in the bin.
On guard online
Spam filters now work well enough that you can make your inbox pretty safe from the porky hordes of messages trying to invade. Wonderful news for the 99% of us who don’t have any use for dodgy meds, fake fashions and pyramid scams. As long as people keep buying into spam and the small group of overlords keeps turning computers into zombies, we’ll need to keep our defences up.
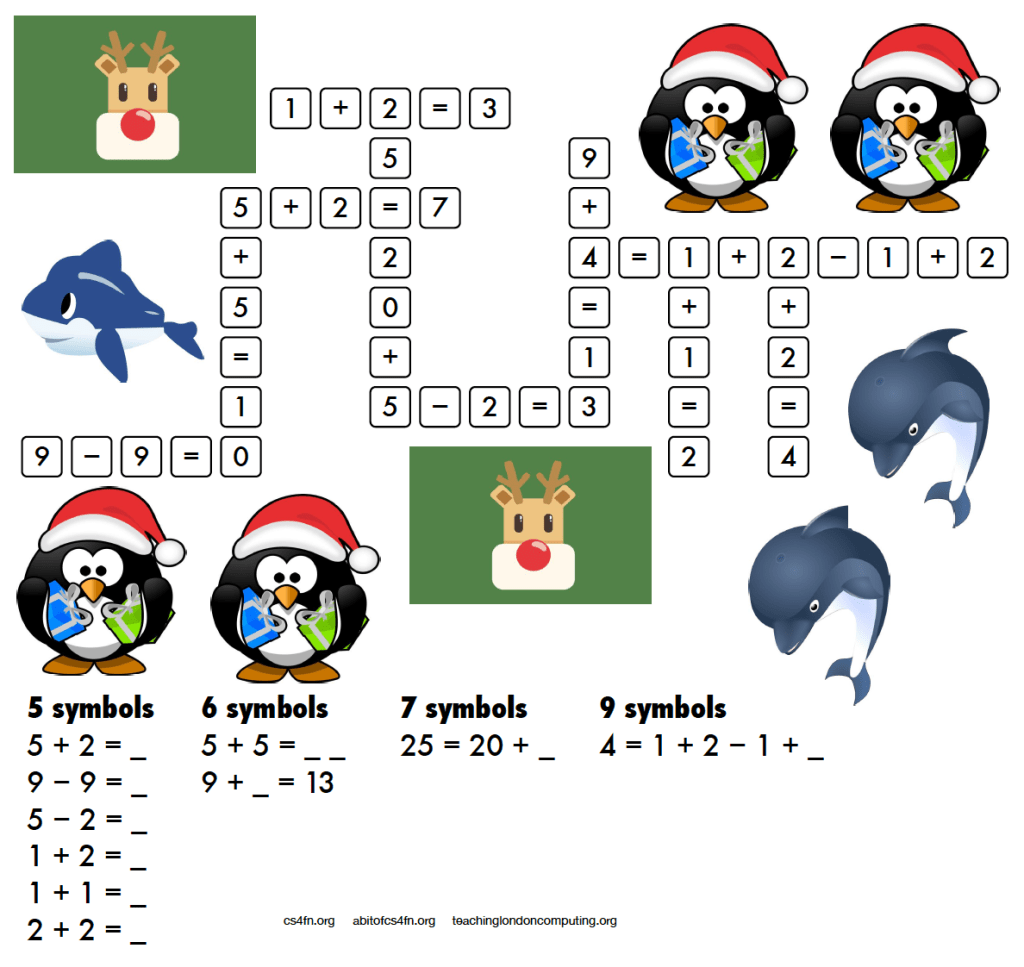
3. Today’s puzzle – the melting snowman
Instructions
One of the snowmen keeps disappearing! Is it melting or just flying
away, and which one is it?
Cut out the picture along the straight black lines, to give three
rectangular pieces. Then follow the simple algorithm and see the
snowman disappear before your eyes.
1. Put the three pieces together in the original positions to make the picture.
2. Count all the snowmen.
3. Swap the position of the top two pieces over so the top and bottom halves of the snowmen line up again
4. Count the snowmen again.
One snowman has disappeared!
Put the pieces back and you will find it reappears.
The explanation and answer will arrive in tomorrow’s (blog) post 🙂
4. Answer to yesterday’s puzzle
Here’s the answer to Daniel’s puzzle.

EPSRC supports this blog through research grant EP/W033615/1.