Welcome to Day 3 of the CS4FN Christmas Computing Advent Calendar. The picture on the ‘box’ was a woolly bobble / pom-pom hat, so let’s see if we can find something computer-ish that might vaguely relate to that in a fairly tenuous way 🙂

Keeping your (computer) cool
Hats help keep your head warm on a chilly day, keeping the warmth IN but computers need to have a way of keeping excess heat OUT to prevent damage to the components (…which are the things creating the heat in the first place of course). You don’t want to fry your graphics card or the Central Processing Unit (the CPU which is your computer’s brain).
I’m your biggest fan
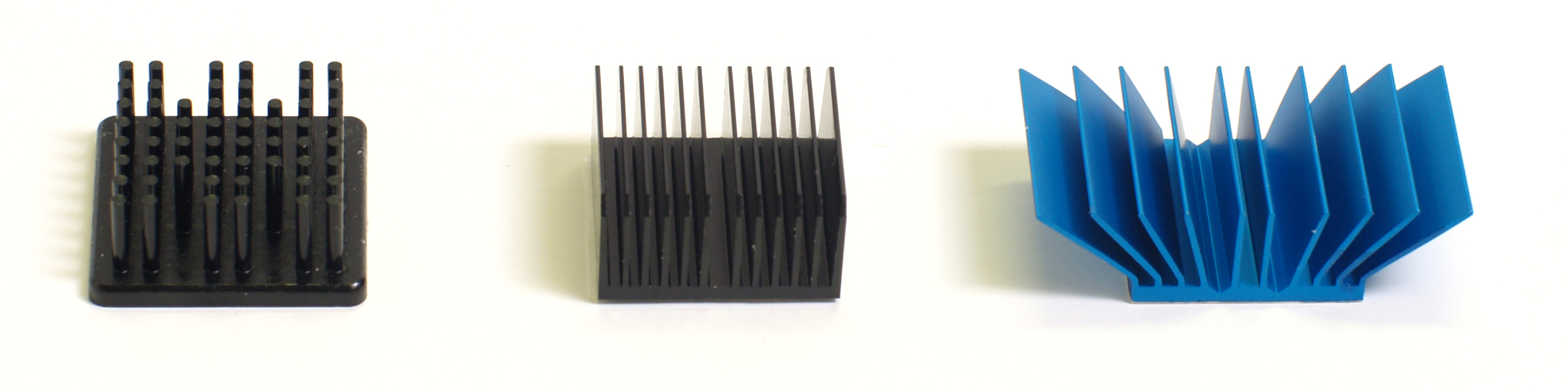
Most computers have a fan which helps regulate the temperature and there are other design features that help heat flow away, including heat sinks which are designed so that a large surface area (which lets heat radiate away) can fit into a small area (see examples below).

Cooling fluids
A much rarer way to remove heat from a computer has been to use a special coolant liquid. In 1985 the Cray-2 supercomputer (which was the fastest computer at the time) was cooled by being immersed in a cooling fluid called Fluorinert which, somewhat ironically, had a very high Global Warming Potential (very similar to the fluorocarbons that were once used to cool fridges).
Reducing power
Another way of keeping computers cooled is to reduce their power so that they generate less heat in the first place. A modern computer in danger of overheating can run its processors and chips at a lower speed.
Bubble Sort
If you want to re-order a bobble hat you can just buy a new one but if you want to re-order lots of bobble hats (that is, put them in a particular order) you might use bobble sort, sorry – bubble sort, to re-order them by size or colour etc.
Bubble sort is an algorithm that lets you work your way through a list of items, comparing any two items and deciding which one goes before the other. You keep going through your list repeatedly until all the items are in the correct order. Computer scientists use lots of different ways to sort information but you can see the bubble sort danced out in the video below.

EPSRC supports this blog through research grant EP/W033615/1.